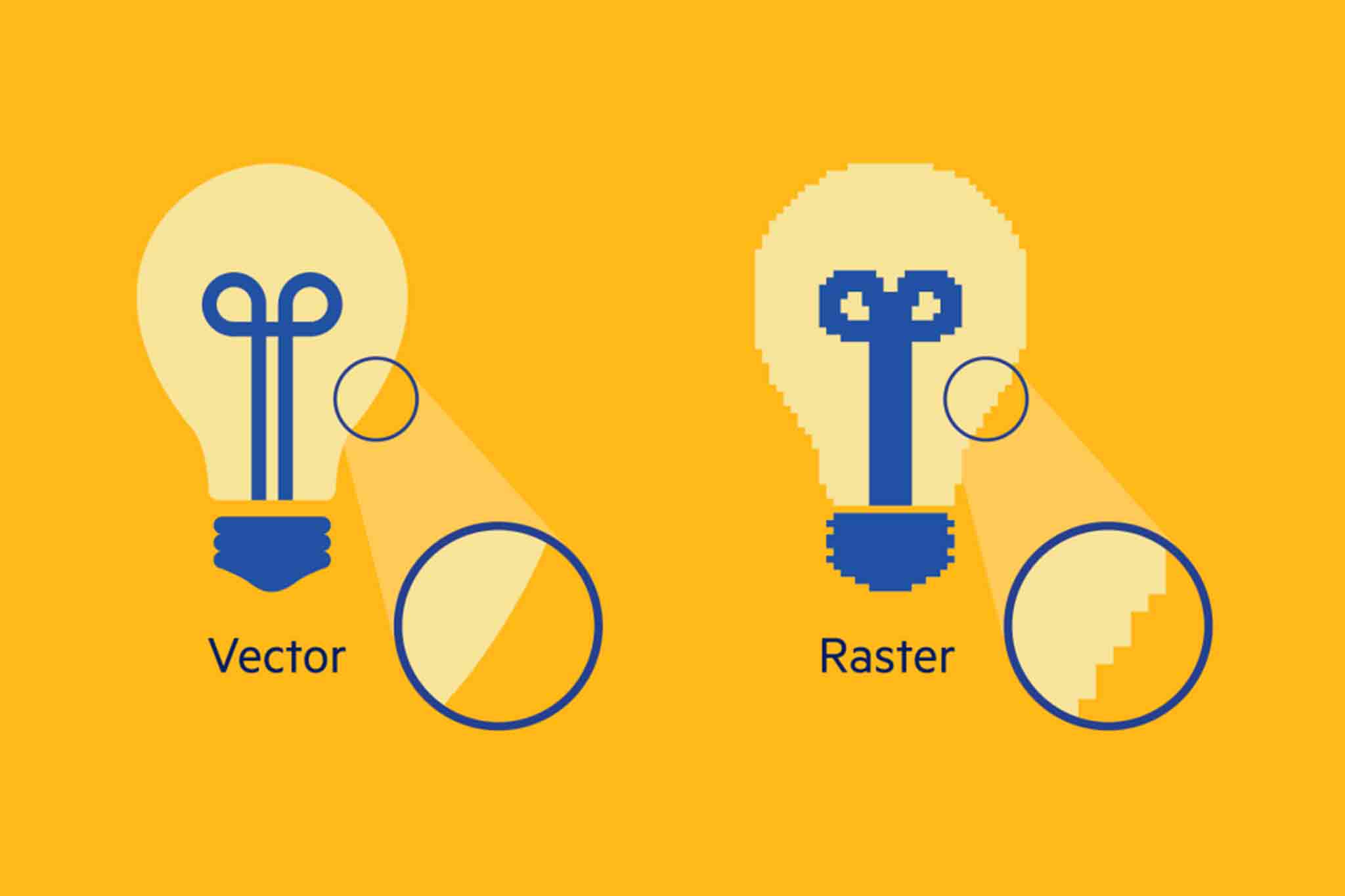
The difference between vector and bitmap
In the realm of digital design and graphics, two fundamental types of images dominate the landscape: vector and bitmap. Each has its own set of characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages, making them suitable for different applications. In this discourse, we’ll delve into the nuances of vector and bitmap graphics, exploring their disparities, applications, and the scenarios in which each excels.
Understanding Vector Graphics:
Vector graphics are comprised of geometric shapes defined by mathematical equations. These shapes include lines, curves, and polygons. Unlike bitmap images, which are composed of pixels, vector graphics are resolution-independent. This means they can be scaled infinitely without losing quality.
Characteristics of Vector Graphics:
- Scalability:Vector graphics maintain their crispness and clarity regardless of size. They can be resized to any extent without sacrificing quality.
- File Size:Vector files are typically smaller in size compared to their bitmap counterparts. This is because they store mathematical formulas rather than individual pixel information.
- Editability:Vector graphics are highly editable since they are constructed using mathematical equations. Elements such as colors, shapes, and sizes can be easily modified.
- Ideal for Illustrations and Logos:Due to their scalability and crispness, vector graphics are commonly used for logos, illustrations, and designs requiring precise lines and shapes.
Understanding Bitmap (Raster) Graphics:
Bitmap graphics, also known as raster graphics, are composed of a grid of pixels. Each pixel contains specific color information, which collectively forms an image. Bitmap graphics are resolution-dependent, meaning they can lose quality when scaled up or down.
Characteristics of Bitmap Graphics:
- Resolution Dependency:Bitmap images are resolution-dependent, meaning their quality is directly tied to their resolution. Enlarging bitmap images can lead to pixelation.
- File Size:Bitmap files can be larger in size compared to vector files, especially for high-resolution images, as they store color information for each pixel.
- Photo Realism:Bitmap graphics excel in depicting complex images such as photographs, as they can capture intricate details and nuances.
- Editing Challenges:While bitmap graphics can be edited using software like Photoshop, they are not as easily editable as vector graphics, especially when it comes to resizing and modifying shapes.

Applications and Use Cases:
-
Vector Graphics:
- Logo Design: Vector graphics are ideal for logo design due to their scalability and ability to maintain clarity across different sizes.
- Illustrations: Artists often use vector graphics for illustrations, as they allow for precise control over shapes and lines.
- Typography: Vector graphics are commonly used in typography to create scalable fonts and text designs.
-
Bitmap Graphics:
- Photography: Bitmap graphics are the preferred format for photographs, as they can capture intricate details and subtle variations in color.
- Digital Art: Artists often use bitmap graphics for digital paintings and drawings, as they offer a wide range of digital brushes and effects.
- Web Graphics: While vector graphics are suitable for logos and icons on websites, bitmap graphics are used for photographs and complex visual elements.
In summary, the distinction between vector and bitmap graphics lies in their underlying structures and characteristics. Vector graphics are defined by mathematical equations, offering scalability and editability, making them ideal for logos, illustrations, and designs requiring precise shapes. On the other hand, bitmap graphics are composed of pixels, offering photo-realistic detail but are resolution-dependent and less editable compared to vectors. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each type of graphic is essential for choosing the appropriate format for specific design tasks and applications.